Breast Cancer Treatment in India
Breast Cancer Treatment in India, oncocare.in, tracking symptoms of Breast Cancer and requesting copies of all your results and information. Your immersion into breast cancer vocabulary, medical appointments and procedures will feel overwhelming. Keeping a journal will ensure you maintain a sense of control throughout your journey.
breast cancer Treatment in India
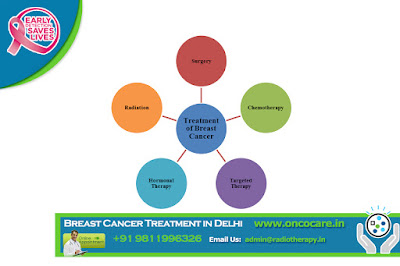
A woman’s most positive course of Breast Cancer treatment will be determined using a number of factors including the size/location of the breast tumor, the stage of the cancer, and laboratory results. Tests that measure Estrogen Receptor (ER) and Progesterone Receptor (PR) are important because the results could be prognostic. These tests can show the potential aggressiveness of the cancer and predict response to treatment. Obtaining a second opinion before beginning breast cancer treatment is recommended. Patients should learn about all treatment options available to them and are encouraged to discuss all possible alternatives with their physician or cancer treatment team. In most cases, women with breast cancer will undergo surgery as part of their cancer treatment. The most common types of breast surgery include: lumpectomy and mastectomy. In addition to a lumpectomy or a mastectomy, some patients will receive adjuvant (additional) treatment to stop cancer growth, spread, or recurrence. Types of adjuvant therapies include: chemotherapy, radiation therapy, and drug treatments. Some women may be treated with chemotherapy, radiation, or drugs without having breast surgery.
Screening Test For Breast Cancer and treatment norms are continually changing. To help clarify your choices, here are 5 questions to ask your doctor:
What are all of my options for testing or treatment for my condition?
How exactly might the treatment help me?
How good is the evidence I’ll benefit from the treatment?
What side effects can I expect, and what bad outcomes might happen?
If it’s a test, what do you expect to learn from it, and how might it change my treatment? If it won’t, why do I need it?
* Recommended by the Lown Institute
Lumpectomy
Lumpectomy refers to the surgical removal of a tumor in the breast along with a small section of the surrounding normal breast tissue. This tissue is then tested for cancerous cells. Lymph nodes may also be removed for testing. If cancerous cells are discovered, additional surgery or treatment may be necessary. Women who undergo a lumpectomy normally receive radiation therapy for about six weeks following the procedure to kill any cancer cells that may have been missed with the removal of the tumor.
Mastectomy
Mastectomy is the surgical removal of the breast. Types of mastectomy include simple, modified radical, and radical. The removal of some or all of the lymph nodes may or may not occur during the mastectomy. In most case reconstruction is possible almost immediately after the surgery. Mastectomy is usually the treatment for women with Stage 0, Stage I, Stage II, or Stage III breast cancers. Surgeons sometimes perform radical mastectomy on Stage IV patients to provide symptom relief.
Auxiliary node dissection is the removal of some or all of the lymph nodes in the underarm. Auxiliary node dissections are usually done on women having a mastectomy to determine if the cancer has spread past the breast. Sentinel node biopsy is when only the sentinel lymph node is removed to estimate breast cancer metastasis (spread). Lymphedema (chronic swelling of the arm) is a potentially dangerous side effect of lymph node removal.
Sentinel lymph node biopsy followed by Breast Cancer Surgery
The sentinel lymph node is the first lymph node to receive lymphatic drainage from a tumor. It is usually the first place that breast cancer will spread to. To identify the sentinel node, an injection of radioactive material or blue dye is given near the tumor. The sentinel node will be the first lymph node to receive the substance or dye. It is then removed and analyzed. If cancer cells are not found, the surgeon will proceed with the removal of the tumor.
Chemotherapy
Chemotherapy is an anticancer drug therapy and is normally given intravenously (through the vein) or orally in pill or liquid form. Chemotherapy may be used on its own or with a lumpectomy or mastectomy. Chemotherapy is a systemic form of treatment; it flows through the bloodstream, affecting the entire body. Its purpose is to obstruct the DNA synthesis of cancer cells. The appropriate combination of drugs used for chemotherapy is based on the patient's cancer type and individual medical profile.
Radiation
Radiation therapy uses high-energy rays to prevent breast cancer cells from growing and dividing. Ionizing radiation leaves energy in the area being treated. This process injures cancer cells by damaging genetic material and stops growth. Even though radiation damages both cancer cells and normal cells, the normal cells are usually able to repair themselves after radiation.
Drug Therapy
A variety of drugs may be used with or without breast surgery to treat breast cancer. The most common breast cancer drug is tamoxifen. It interfers with the estrogen receptors in breast cancer cells. By blocking estrogen in the breast, tamoxifen helps reduce the growth and reproduction of breast cancer cells.Other drugs may be used with or without breast surgery to treat breast cancer. They include:
Herceptin: used to treat breast cancer patients who are Human Epidermal growth factor Receptor 2-positive (HER2 )
Ellence: used in conjunction with chemotherapy (cyclophosphamide and fluorouracil) to treat early stage breast cancer
Taxol: used to treat early and advanced stages of breast cancer
Docetaxel: used in conjunction with chemotherapy to treat advanced breast cancer
Aromasin: used in post-menopausal breast cancer patients with advanced breast cancer
Arimidex: used in advanced (metastatic) breast cancer patients who have not responded well to tamoxifen
No comments:
Post a Comment